TypeScript
TS 认识
1、概念
是属于 JS 的超集,支持所有 JS 的语法,然后新增加了其他内容,比如类型约束、接口、泛型、枚举等。
TS 需要先编译为 JS ,然后才能运行。
2、环境搭建
bash
>> 全局安装 ts 的 cli
npm i -g typescript
# 检查版本
tsc -v
# 编写 index.ts 文件
# 编译
tsc index.ts
>> vue 项目
在配置项目的时候选择 ts 。项目搭建流程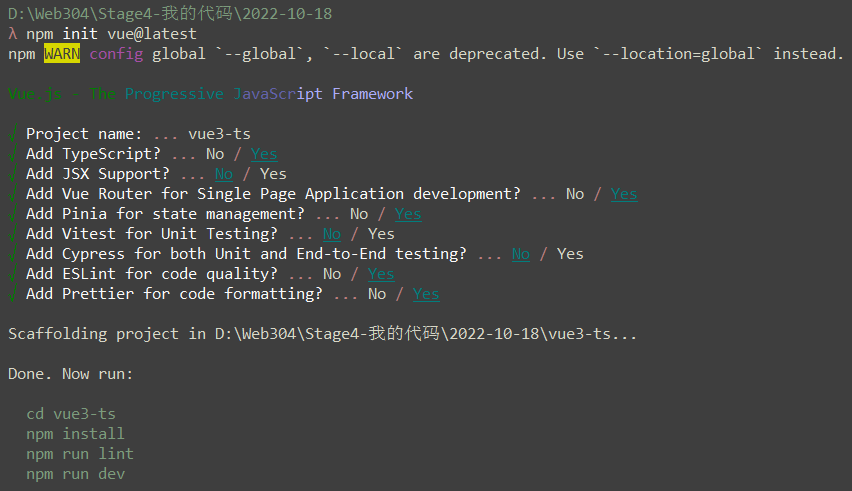
类型约束
在 ts 中声明的变量(或者函数的参数等)都会进行类型约束,不同类型的数据之间不能赋值。
使用:指定变量类型。
tsx
1、字符串类型
let str: string = 'abc';
str = '123';
2、number类型
let str: number = 123;
3、布尔值类型
let bool: boolean = true;
4、symbol 类型
let sy: symbol = Symbol();
5、null 和 undefined 类型
6、any 类型
该类型可以被赋予任何类型的值。
7、void 类型
没有任何类型,在函数没有返回值的时候使用。
function foo(): void {
console.log();
}
8、never 类型
永远不会存在值的类型
9、unknown10、元组类型( Tuple )
用于定义具有有限数量的未命名属性的类型,使用元组时必须提供每个属性的值。
tsx
let tu: [string, number] = ['abc',123];
// 访问的方式与数组的访问方式一样
tu[0]
// 通过 push 不会报错
tu.push(123);11、枚举类型( Enum )
用于组织收集一组相关变量的方式,可以非常清晰地去表达意图。
tsx
// 数字枚举
enum Color {
Red, // Color.Red 表示 0
Green, // Color.Green 表示 1
Blue // Color.Blue 表示 2
}
const num : Color = Color.Red;
console.log("Color.Red - ",num); // Color.Red - 0
// 也可以设置枚举成员的初始值,可以递增
enum Color {
Red = 1, // Color.Red 表示 1
Green, // Color.Green 表示 2
Blue, // Color.Blue 表示 3
Yellow // Color.Yellow 表示 4
}
// 字符串枚举,所有枚举成员都必须给初始值
enum Role {
Admin = 'admin',
User = 'user'
}
// 字符串枚举和数值枚举混合枚举
enum Hun {
A, // 0
B, // 1
C = 'c',
D = 'd',
E = 6, // 在字符串枚举之后的数值必须给初始值
F // 7
}枚举作用:给数值或者其他数据进行语义化,提高代码的可读性。
12、接口
接口是对行为的抽象。
tsx
// 语法
interface 接口名 { // 接口名建议大驼峰
属性: 属性类型;
}
// 约束对象
interface Props {
path: string;
name: string;
}
const obj: Props = {
path: '/login',
name: 'login'
}
console.log(obj);
// 约束数组
interface Props {
// key 约束为 number,即表达数组, key 任意命名就可以
[key: number]: string;
}
// 约束方法
interface Props {
path: string;
name: string;
foo: () => void; // foo 是一个方法,没有返回值,没有参数
}
const obj: Props = {
path: '/login',
name: 'login',
foo() {}
}
console.log(obj);
// 可选属性
interface Props {
path: string;
name: string;
title?: string;
}
// 只读属性
interface Props {
path: string;
name: string;
readonly title: string;
}
// 任意属性
interface Props {
path: string;
name: string;
[key: string]: any;
}
const obj: Props = {
path: '/login',
name: 'login',
meta: 123
}
console.log(obj);
// 接口继承
interface PropsA {
path: string;
}
interface PropsB extends PropsA {
name: string;
}
const odj: PropsB = {
path: '',
name: ''
}13、类型别名
用于给一个类型取一个新名字,和接口有点类似,可以用于原始类型、接口联合等等。
tsx
type Name = string;
type Name = string | null; // 联合类型,或者两个类型之一
type Foo = () => string; // 约束函数,没有参数,返回值是 string
type Resolve = Name | Foo;
type IProps = {
url: string;
foo: () => void;
}
// 交叉类型
interface IPA {
x: number;
}
interface IPB {
y: number;
}
type IP = IPA & IPB;14、JS 内置对象
在 JS 中有很多内置对象,可以直接用于 TS 的类型约束。
String
Function
Document
HTMLElement(包含HTMLInputElement、Event、MouseEvent)
15、函数
tsx
function foo(x: number,y: number): number {
return x + y;
}
const foo: (x: number,y: number) => number = function(x: number,y: number): number {}
// 简写
const foo: (x: number,y: number) => number = function(x, y) {}
// 结合 type
type FnProps = (x: number,y: number) => number;
const foo: FnProps = function(x, y) {}
// 可选参数
function foo(x: number, y: number, z?:number): number {
return x + y;
}
// 参数默认值
function foo(x: number = 0,y: number = 0): number {
return x + y;
}16、数组
tsx
// 约束数组
// 方式1:
const arr: string[] = ['a', 'b'];
// 方式2:
const arr: Array<string> = ['a', 'b'];
// 方式3:
interface AP {
[key: number]: string;
}
const arr: AP = ['a', 'b'];
// 复杂数组
interface IProps {
name: string;
path: string;
}
const arr: IProps = [{
name: '',
path: ''
}];运算符
1、非空断言 !
一般用在变量名或者函数之后,用于强调对应的元素是非 null 或者 undefined 。
tsx
function foo(callback?: () => void){
callback!(); // callback()一定存在
})2、链运算符 ?
用来判断左侧的表达式是否为 null 或者 undefined ,如果为空就不执行,否则执行后面的代码。
tsx
a?.b() // 如果a存在就会调用b
// 类似
success && success()3、类型断言
确定知道某个变量的类型。
tsx
// 写法1 - <类型>值
function isFish(animal: Cat | Fish) {
if (typeof (<Fish>animal).swim === "function") {
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 该写法在 react 中会有问题
// 写法2 - 使用 as 关键字
function isFish(animal: Cat | Fish) {
if (typeof (animal as Fish).swim === "function") {
return true;
}
return false;
}class
tsx
class Person {
name: string; // 默认公开属性
public age: number; // public 表示公开属性
private height: number = 160; // private 私有属性,只能在类的内部使用,子类和实例都不能使用
protected city: string = "成都"; // protected 受保护的,可以在子类中访问,但是实例不能访问
static version = "v1"; // 静态属性,只能通过类名调用
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
// 构造函数
this.name = name; // name 是加在实例上的
this.age = age;
}
sayHi() {
console.log(this.height);
}
get birth() {
// get 方法
return 1990 + this.age;
}
set birth(a: number) {
// set 方法
this.age = a;
}
}
// 继承
class Student extends Person {
constructor(name: string, age: number) {
super(name, age);
}
}
// 抽象类 - 只能被继承,不能被实例化,一般用于抽象类中的公共代码
abstract class Animal { }
class Cat extends Animal { }
new Cat();
// 类也可以继承接口
interface PersonProps {
name: string;
}
class Admin implements PersonProps {
name: string = "admin";
}泛型
1、说明
泛型是指在定义函数、接口或者类的时候,不预先指定具体的类型,而是在使用的时候再指定类型的一种特性。
简单理解就是给类型变成一个变量。
2、案例
tsx
function id(value: number): number {
return value;
}
id(123);
function idS(value: string): string {
return value;
}
idS('abc');
function idA(value: any): any {
return value;
}
// 优化,使用一个 T 去表示一个类型
function id<T>(value: T): T {
return value;
}
// 使用的时候在指定类型
id<number>(1);
id<string>('abc');3、泛型的定义
泛型使用 <> 进行定义,使用 A - Z 来定义泛型变量,常见的为 T, K, U
4、其他泛型定义
tsx
function foo<T, U>(x: T, y: U): void {
// ...
}
foo<string, number>('abc', 123);
function foo<T>(arg: Array<T>) {}
interface Props<T> {
name: string;
children: T;
}
class Cat<T = any> { // 泛型默认值
type: T;
constructor(type: T) {
this.type = type;
}
}
// 泛型继承
function foo<T extends Date>(arg: T) {}插件
- Volar(vscode插件)
- Vue 3 Snippets / Vue VSCode Snippets(vscode插件)
- Vue.js devtools beta(浏览器插件)
