一、数据库的种类
关系型数据库、非关系型数据库(nosql)
都是存的表结构
二、数据库的数据类型
1、整数类型int
2、浮点数类型和定点数类型float、double
3、字符串类型char、varchar
4、日期与时间类型date、datetime
三、数据库的基本操作
1、创建数据库
1)、通过编辑器创建数据库
2)、通过sql语句创建
create database 数据库名称;2、查看数据库
show create database 数据库名称;3、删除数据库
drop database 数据库名称;4、查看所有数据库
show databases;5、数据库的字符集修改
alter database 数据库名 character set gbk;6、切换数据库
use 数据库;7、查看当前使用的数据库
select database();四、数据表的基本操作
1、创建数据表
create table 表名(
字段1 字段类型,
字段2 字段类型,
...
字段n 字段类型
);2、查看数据表
-- 查看当前数据库中所有表
show tables;
-- 查看表的基本信息
show create table 表名;
-- 查看数据表的字段信息
desc 表名;3、修改数据表
-- 修改表名
alter table 原先的表名 rename to 修改后的表名
-- 修改字段名
alter table 表名 change 原先字段名 修改后的字段名 字段类型;
-- 修改字段数据类型
alter table 表名 modify 字段名 字段类型;
-- 增加字段
alter table 表名 add 字段名 字段类型;
-- 删除字段
alter table 表名 drop 字段名;4、删除数据表
drop table 表名;五、数据表的约束
1、主键约束
用于唯一标识对应的记录
字段名 数据类型 primary key;-- 例子:
-- 第一种方式
create table student(
id int primary key,
name varchar(20)
);
-- 第二种方式
create table student(
id int,
name varchar(20),
primary key(id)
);2、非空约束
字段名 数据类型 not null;3、默认值约束
字段名 数据类型 default 默认值;4、唯一性约束
字段名 数据类型 unique;5、外键约束
-- 创建数据表时
constraint foreign key (从表外键字段) references 主表 (主键字段);
-- 创建数据表后
alter table 从表名 add foreign key (从表外键字段) references 主表 (主键字段);
-- 删除外键
alter table 从表名 drop foreign key 外键名;创建表:给从表添加外键约束后,应该先创建主表(班级表),然后再创建从表
添加数据:先添加主表的数据 ,然后添加从表的数据
删除数据:先删从表数据,然后删除主表数据
删除表:先删除从表,然后删除主表
-- 例子:
-- 外键应该怎么加呢?添加外键前要清楚:这两张表哪张是主表?哪张是从表?
-- 从两张表的关系来区分:表关系有一对一、一对多、多对多
-- 一对多的关系:学生表和班级表,班级表是一,学生表是多
-- 班级表就是主表,学生表就是从表
-- 班级表
create table class (
cid int auto_increment primary key(cid),
classname varchar(8)
)
-- 学生表
create table student (
stuid int primary key auto_increment,
stuname varchar(8) unique not null,
sex varchar(2) default '男',
classid int not null references class(cid),
constraint foreign key(classid) references class(cid)注意:
1、从表里的外键通常为主表的主键 2、从表里外键的数据类型必须与主表中主键的数据类型一致 3、主表发生变化时应注意主表与从表的数据一致性问题
6、自增
auto_increment六、数据操作
1、添加数据
insert into 表名(字段名1,字段名2,...) values (值1,值2,...);- 每个字段与其值是严格一一对应的
-- 例子:
-- 为表中所有字段插入数据
insert into student values
(1,'呆呆','女',4),
(2,'朱朱','女',1),
(3,'拢龙','男',6)
-- 为表中指定字段插入数据
insert into student (id,name,age) values (4,'拢龙',3);2、删除数据
delete from 表名 [where 条件表达式];
truncate table 表名;注:where代表条件,如果没有条件将会删除该表所有数据。
delete 可以通过日志恢复,truncate table 不能通过日志恢复。
1、delete语句后可跟where子句,可通过指定where子句中的条件表达式只删除满足条件的部分记录;但是,truncate语句只能用于删除表中的所有记录。
2、使用truncate语句删除表中的数据后,再次向表中添加记录时自动增加字段的默认初始值重新由1开始;使用delete语句删除表中所有记录后,再次向表中添加记录时自动增加字段的值为删除时该字段的最大值加1。
3、delete语句是dml语句,truncate语句通常被认为是ddl语句。
3、改数据
update 表名 set 字段名1=值1[,字段名2 =值2,…] [where 条件表达式];七、数据表简单查询
-- 查询所有字段
select * from 表名;
-- 查询指定字段
select 字段名1,字段名2... from 表名;
-- 常数的查询
select 常数 from 表名;
-- 从查询结果中过滤重复数据
-- 在select查询语句中distinct关键字只能用在第一个所查列名之前
select distinct 字段名 from 表名;
-- 在select查询语句中还可以使用加减乘除运算符
-- 例子:
select name,age+10 from student;八、函数
1、聚合函数
- 使用规则:只有selete子句和having子句、order by子句中能够使用聚合函数。例如,在where子句中使用聚合函数是错误的。
1)、count()
统计表中数据的行数或者统计指定列其值不为NULL的数据个数
2)、max()
计算指定列的最大值
3)、min()
计算指定列的最小值
4)、sum()
计算指定列的数值和
5)、avg()
计算指定列的平均值
2、其他函数
1)、时间函数
select now();
select day (now());
select date (now());
select time (now());
select year (now());
select month (now());
select current_date();
select current_time();
select current_timestamp();
select addtime('14:23:12','01:02:01');
select date_add(now(),interval 1 day);
select date_add(now(),interval 1 month);
select date_sub(now(),interval 1 day);
select date_sub(now(),interval 1 month);
select datediff('2019-07-22','2019-05-05');2)、字符串函数
-- 连接函数
select concat()
--
select instr()
-- 统计长度
select length()3)、数学函数
-- 绝对值
select abs(-136);
-- 向下取整
select floor(3.14);
-- 向上取整
select ceiling(3.14);九、条件查询
-- 使用关系运算符查询
select * from student where stuAge > 16
-- in
-- 包含
select * from student where stuAge in (4,1,6)
select * from student where stuAge not in (4,1,6)
-- between and
-- 注意范围查询between是要包含16和20的
select * from student where stuAge between 16 and 20
select * from student where stuAge not between 16 and 20
-- 空值
-- 注意:查询为空,不能使用 = 去比较,要使用is null
select * from student where stuAge is null
select * from student where stuAge is not null
-- and
select * from student where stuAge > 16 and stuAge < 20
-- or
-- 或者
select * from student where stuAge = 16 or stuName = '呆呆'
-- like
-- 模糊查询
select * from student where stuName like '朱%' // 以"朱"开头
like '%朱' // 以"朱"结尾
like '%朱%' // 包含"朱"
-- _:只匹配一个字符,%:后面有字符或者前面有字符
select * from student where stuName like '%朱_'
select * from student where stuName like '朱_'
-- limit
-- 返回限定行,只有一个数字的情况是从第0条开始
-- 有两个数字:第一个代表开始的下标,第二个代表返回几条
select * from student where sex = '女' limit 0,3
-- group by:投影列只能是聚合函数列或者是分组列
select stuAge, classId from student group by classId
-- order by排序
-- asc:升序,desc:降序
-- 查询所有学生。降序排列,默认是升序排列
select * from student order by stuAge desc
select * from student order by stuAge asc十、别名设置
1、为表取别名
select * from 表名 [as] 表的别名 where ...;2、为字段取别名
select 字段名1 [as] 别名1,字段名2 [as] 别名2,... from 表名 where ...;十一、多表连接查询
1、交叉连接查询(笛卡尔连接)
select * from 表1 cross join 表2;2、内连接查询
-- inner join:连接两个表,on:连接条件,inner可以省略
select 查询字段1,查询字段2, ... from 表1 [inner] join 表2 on 表1.关系字段=表2.关系字段3、外连接查询
-- 外连接又分为左(外)连接和右(外)连接
-- 关键字左边的表被称为左表,关键字右边的表被称为右表,outer可以省略。
-- 1、left [outer] join 左(外)连接:返回包括左表中的所有记录和右表中符合连接条件的记录。
-- 2、right [outer] join 右(外)连接:返回包括右表中的所有记录和左表中符合连接条件的记录。
select 查询字段1,查询字段2, ... from 表1 left | right [outer] join 表2 on 表1.关系字段=表2.关系字段 where 条件;十二、子查询
-- 查询所有学生信息以及班级
-- 相关子查询
select *,(select className from class where cid = classId) from student
-- 查询一班的学生有哪些
-- 非相关子查询
select * from student where classId = (select cid from class where className = '一班')1、比较运算符
select * from class where cid = (select classid from student where sname='呆呆');2、exists
-- exists关键字后面的参数可以是任意一个子查询,它不产生任何数据只返回true或false。当返回值为true时外层查询才会执行。
select * from class where exists (select * from student where sname='呆呆');3、all
-- 带all关键字的子査询返回的结果需同时满足所有内层査询条件
-- all没有办法查询null
-- 比所有都大
select * from student where stuAge > all (select stuAge from student where sex = '男')4、any
-- any关键字表示满足其中任意一个条件就返回一个结果作为外层查询条件
-- 比任意一个大的
select * from student where stuAge > any (select stuAge from student where sex = '男')十三、总结
-- 查询语句的书写顺序和执行顺序
select => from => where => group by => having => order by => limit
-- 查询语句的执行顺序
from => where => group by => having => select => order by => limit十四、数据库设计
1、数据库设计的三大范式
第一范式:数据库中所有的字段值都是不可分解的原子值。
第二范式:先满足第一范式,确保表中的每一列都和主键相关,即每一个表只描述一件事。
例子:学生表中就不会把学生名字和班级名字放在一个表中。
第三范式:先满足第二范式,表中所有的非主键必须和主键之间相关,而不能间接相关。
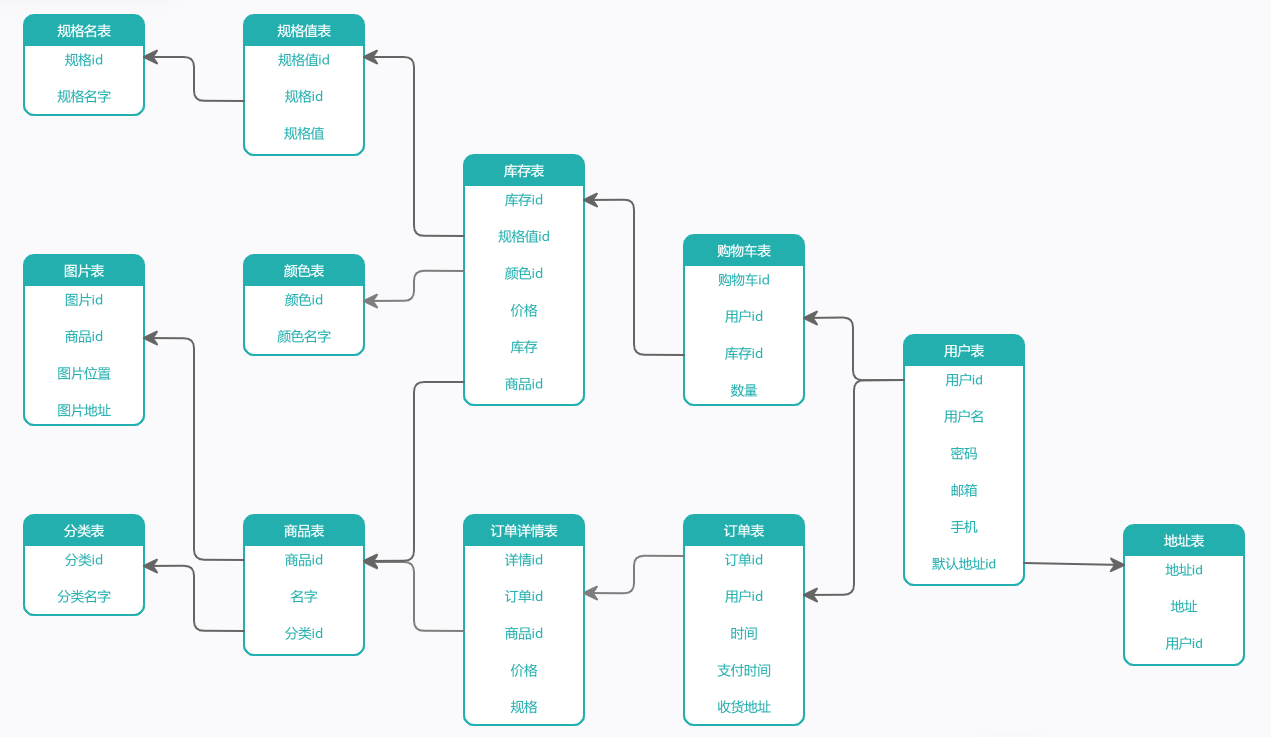
2、一般电商系统的数据库设计